What is irritable bowel syndrome Causes and Treatment
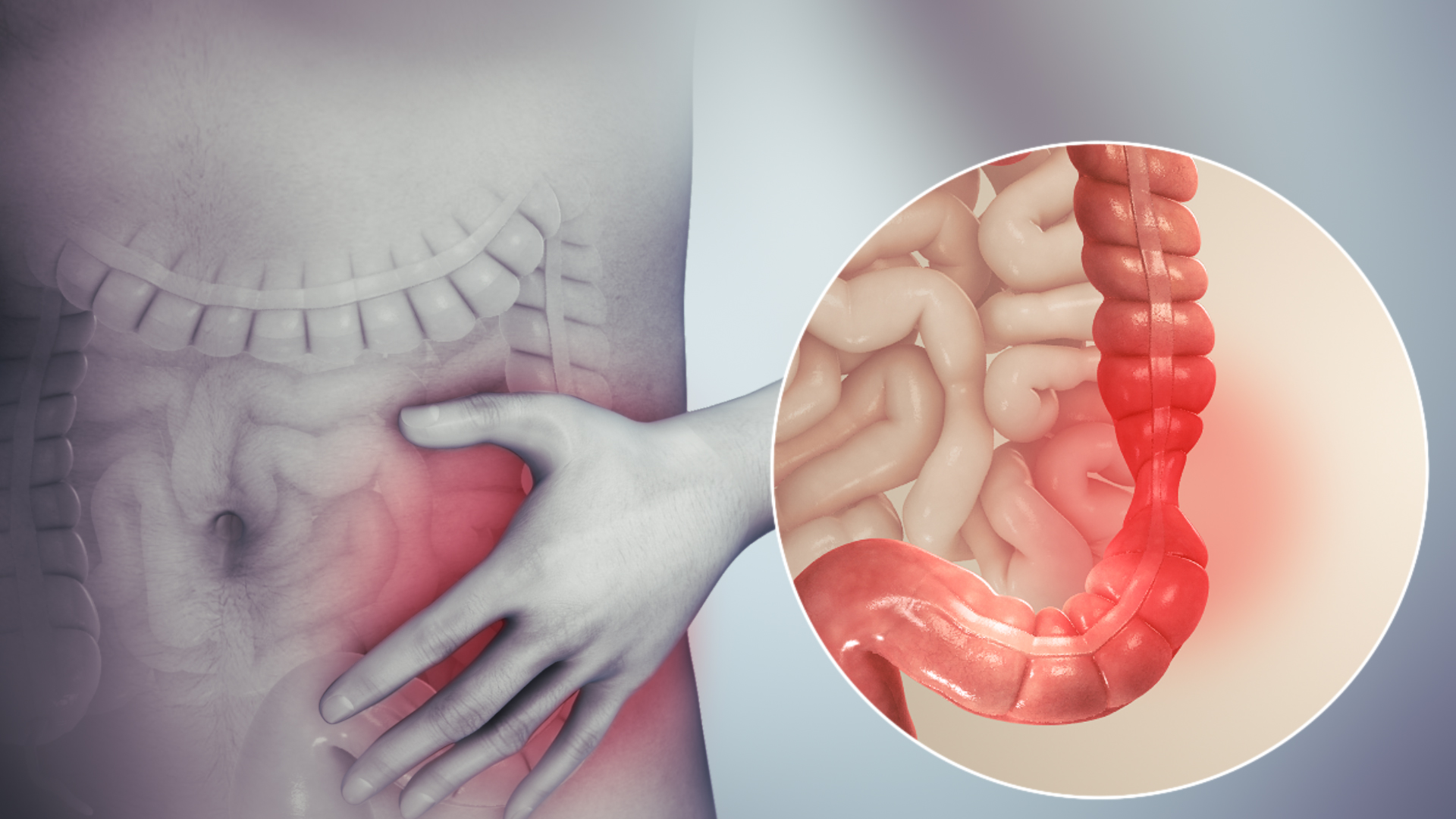
IBS is a disorder that affects the gastrointestinal tract, and it can cause discomfort in your abdomen. It’s also known as spastic colon or mucous colitis-the name depends on what type of IBS you have! This condition does not lead to severe complications but may impact the quality of life by causing distress.
IBS is a separate condition from inflammatory bowel diseases that may not affect the intestines. IBS rarely causes intestinal damage and does not increase the risk of gastrointestinal cancers, but it can severely impact the quality of life. Treatment for this disease includes drug therapies, dietary changes, or psychotherapy to help sufferers manage their symptoms better. Hence, they can live more comfortable lives with less pain and discomfort.
IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) has been given its own classification as an independent disorder rather than being grouped with other digestive issues like Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD). This means that while there are some similarities between these two conditions – such as abdominal cramping and diarrhea- IBD will often result in severe inflammation throughout.
What are the symptoms?
IBS also called ‘spastic colon,’ is a collection of symptoms that many people experience. Some people have persistent IBS while others find it comes and goes:
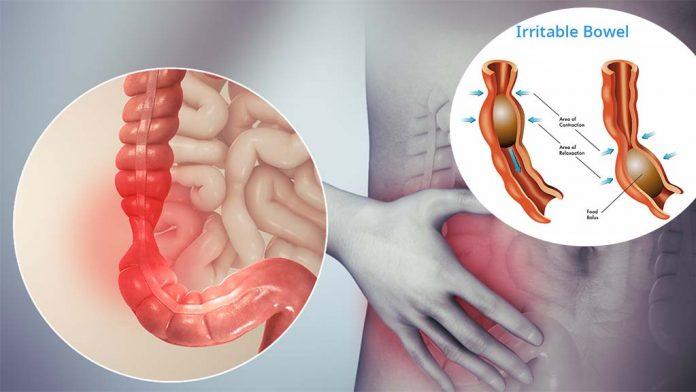
The main symptom of spastic colitis is abdominal pain and cramping with altered bowel patterns such as diarrhea or constipation either alone or in combination; other symptoms may include bloating, nausea, vomiting blood from rectal bleeding (hematochezia), lack of appetite for food or weight loss. Prolonged stress can trigger the syndrome to flare up more frequently than normal. Still, not everyone has this reaction – some can manage their anxiety through lifestyle changes like meditation instead. There’s no cure yet, so treatment tries to control your diet by limiting dairy products.
- Abdominal pain that improves after pooing
- Constipation/diarrhea that may come in alternating patterns
- Bloating
Types of IBS
Irritable bowel syndrome is a condition that can be divided into three categories based on whether diarrhea or constipation are the most common. The first category, IBS with predominant diarrhea (IBS-D), includes at least one day of loose stools per week and fewer than 3 days in which they experience hard stool passage each month. In patients where there are equal amounts of both types of feces produced throughout the day, it may be categorized as either IBS with mixed abdominal symptoms (IBS-M) or unclassified irritable bowel syndrome if no other cause for their problems has been found after extensive testing.
- Diarrhea-predominant IBS (IBS-D) is a severe and chronic form of irritable bowel syndrome. The most common subtype, it comes with frequent stool movements that are often urgent in need to be defecated along with loose watery stools. Diarrhea predominate patients have an increased risk for developing fecal incontinence as well as diarrhea related complications such as malnutrition or dehydration from not being able to keep their bowels under control long enough before urgently going again when the person has had too much fluid intake.
- Constipation-predominant IBS (IBS-C) is a common form of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. It can be characterized by stomach pain, bloating and delayed or infrequent bowel motions. Stools are harder than usual and very lumpy, leading to constipation that often leads to gas as well!
- IBS-M can be a tricky disease to diagnose and treat because it is not always diarrhea during the day or night.
There are many different medications for mental illness, so it is important to see a doctor.
How common is IBS?
Irritable bowel syndrome is the most common gastrointestinal disorder, and up to 20% of people will experience IBS in their lifetime. However, it affects more women than men, with twice as many females experiencing symptoms. The condition can be debilitating for sufferers who often feel anxious or embarrassed about discussing their problem openly because there isn’t any known cure yet – only treatments that help manage symptoms like pain relief medications and dietary changes.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic digestive system disease affecting approximately 10-20% of the population. It’s been found that while incidence rates are equal among both genders, female patients comprise two times as many cases when compared against males due to an increased likelihood of hormonal factors being linked to its development.
- Below the age of 45
- With an existing psychological illness
- Who are female (5)
- Living in a Western country or South America
How is IBS Diagnosed?
No one bothered to think of a way to diagnose the painful stomach disorder, IBS. It is such an elusive affliction that there are no physical damages or abnormalities in your intestines, and it’s often diagnosed based on how many days per week you have intestinal pain for at least 3 months with 2 symptoms from this list:
1) abdominal discomfort relieved by defecation; 2) mucus evacuated along with stool (i.e., diarrhea); 3) uncomfortable bloating, feeling full even though not overly hungry 4). urgency-frequency syndrome – having more than three bowel movements every day 5)…
- Change to abdominal pain with pooing (defecation)
- Change in pooing (defecation) frequency
- Change in appearance of poo (stools) (7)
Where do symptoms of IBS come from?
Symptoms of IBS come from a miscommunication between the brain and the gut. During digestion, our intestines contract and relax to move contents towards the anus – which is usually painless- but can lead to painful symptoms such as cramping or abdominal pain. The altered signals from your brain may also affect how fast food moves through your intestine (motility), leading you into constipation or diarrhea phases.